GMS test and certification process/cycle/version type/test content
1.GMS Certification Purpose
The purpose of GMS certification is to ensure that devices comply with Google Mobile Services standards to ensure that applications and services provided by Google run stably on the device and provide users with a consistent experience.
GMS certification helps device manufacturers and developers gain access to the Google ecosystem and ensures that their devices are widely accepted in the marketplace. (GMS is known as Google Mobile Service.)

2.GMS Certification Process
2.1. Sign the contract
2.2. Authorisation agreement submitted to Google for approval
2.3.Software property checking and modification
2.4. After Google‘s approval, integrate clinetid and submit case opening report.
2.5. Apply for Google key
2.6. Start complete testing
2.7. Import key verification
2.8.Software debug, solve all problems, new version test
2.9.Self-test passed
2.10. Start formal testing, complete Google approved
3.Testing Cycle
Start the complete test to solve all the problems, self-test pass need about 1-2 months, generally according to the project problem situation and software debugging speed. Formal testing for a week, Google approved 2-3 weeks.
4. Version type
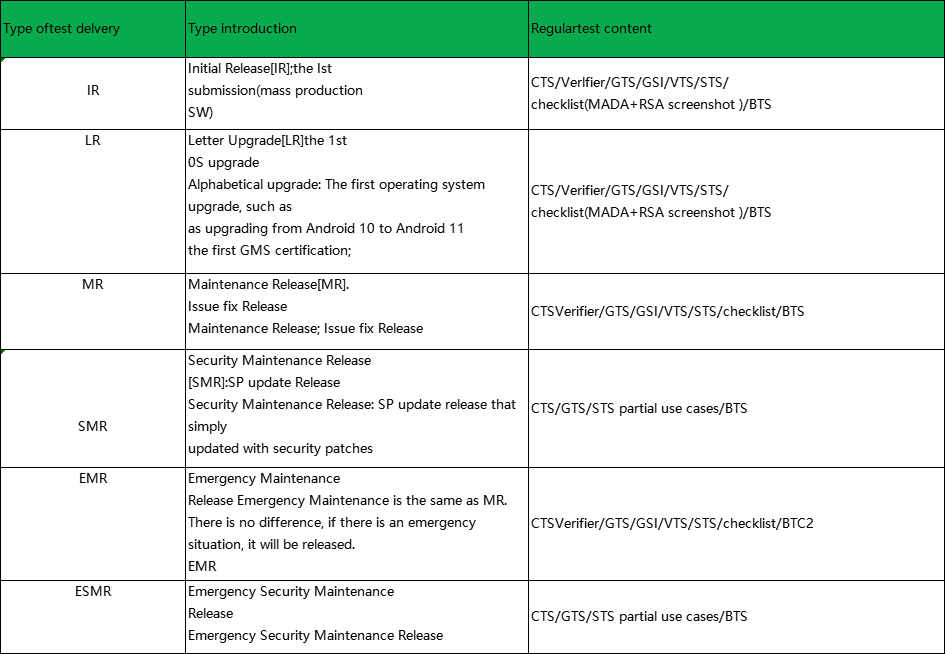
4.1.EMR and ESMR refers to the customer‘s internal emergency version of the fastest speed outgoing, not Google‘s EMR process.
4.2.Google‘s EMR process is very slow generally does not apply.
4.3.RSA is a separate agreement signed by Google and OEMs, and can be ignored without signing it.
4.4.Android 14 mobile phones need additional testing AACT.
5. Test content
CTS: Android platform compatibility, CDD + Android SDK/NDK/APIs.
GTS: Verify whether GMS applications are correctly integrated, streaming media playback, etc.
STS: Test security patch integration.
VTS: Test HAL, driver and kernel after replacing GSI.
CTS-ON-GSI: Test compatibility after replacing GSI.
CtsVerifier: Supplementary test to CTS test, manual judgement is required.
BTS: Package uploaded to Google server to scan for hazardous applications, security patches, application permissions.
MADA checklist : Manual testing of GMS application prefabrication and location, boot wizard, etc.
6. Common protocols
NDA agreement full name: Non-Disclosure Agreement.
AFA agreementfull name: Anti-Fragmentation Agreement, translated as Anti-Fragmentation Agreement, the production of Android products must be certified by GMS.
MADA agreement full name: Mobile Application Distribution Agreement, Mobile Application Distribution Agreement.
EDLA agreementfull name: Enterprise Device Licensing Agreeement, Enterprise Device Licensing Agreeement, MADA agreement supplement.
Recommended items
-

Deeplight Google EDLA testing actual project experience sharing and Google EDLA certification detailed process
Google Android devices over the authentication is to do MADA or EDLA?What is the difference between EDLA and MADA? How to determine which certification protocol should be chosen for the device?View more -

Deeplight Google Android System GMS MADA Certification service
Google‘s Android system is one of the most important operating systems at present and is widely used in various terminal devices. In order to ensure the smoothness of the Android system, Google has developed an automatic testing process and a manual testing process to make the system run stably....View more -

Detailed interpretation of Google GMS certification, what is Google GMS certification, how to do GMS certification?
Google places a number of requirements on device manufacturers (known as OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers)) who wish to sell mobile devices with GMS installed. To ensure these requirements are met, Google has a manufacturer licensing process and requires certification of products for sale....View more




