Wi Fi 5, Wi Fi 6, Wi Fi 6E, and Wi Fi 7 RF testing services
Wi Fi 5 refers to operating in the 5GHz radio frequency band.
Wi Fi 6 is a wireless LAN technology created by the Wi-Fi Alliance in the IEEE 802.11 standard. It improves the uplink and power management of all supported frequency bands (2.4GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz), and is suitable for routers and devices in homes and workplaces, as well as smart home IoT devices.
Wi Fi 6E is a new field of Wi Fi 6 technology that can operate at a speed of 9.6 Gbps in the 6GHz frequency band. The ‘E‘ in Wi Fi 6E represents Extended, which refers to the extension of the available frequency range. Many of these countries have already opened up Wi Fi 6E, such as the United States, South Korea, the United Kingdom, Brazil, the European Union, and Chile. The United States, South Korea, Brazil and Chile can fully use 5925-7125MHz spectrum. The UK and EU can only use the 5925-6425MHz spectrum.
Wi Fi 7 has also doubled the bandwidth of the 6GHz frequency band, giving it a potential speed of 46.1Gbps.
.png)
1、 The main differences between Wi Fi 5, Wi Fi 6, Wi Fi 6E, and Wi Fi 7
1) Frequency band: Wi Fi 5 only covers 5 GHz, while Wi Fi 6 covers 2.4/5GHz. Wi Fi 6E extends the functionality of Wi Fi 6 from the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands to the 6 GHz frequency band, providing up to 1200 MHz, while Wi Fi 7 supports three frequency bands: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz;
2) Modulation mode: Wi Fi 6 and Wi Fi 6E support 1024-QAM higher than Wi Fi 5‘s 256-QAM, with higher data capacity and faster transmission speed. Wi Fi 7 supports 4096-QAM;
3) Bandwidth: Wi Fi 5 operates in high frequency bands above 5GHz, and can increase bandwidth to 40MHz or even 80MHz or higher. Wi Fi 6 and Wi Fi 6E have a bandwidth of 160 MHz, while Wi Fi 7 has a bandwidth of up to 320 MHz;
2、 What testing services can we provide and their advantages
(1) Non signaling testing of Wi Fi 6E and Wi Fi 7 using a wireless communication tester
a) First-class measurement accuracy and optimized testing time using downlink broadcasting and cross access technology;
b) Quickly integrate computer technology to ensure excellent testing performance;
c) Combining a comprehensive vector signal analyzer/vector signal generator integrated testing product;
d) RF frequency up to 8GHz, 320MHz bandwidth;
e) In receiver testing/device under test reception testing, broadcast mode supports synchronous transmission across all RF ports/outputs;
f) Satisfy customers‘ requirements for the performance, utilization, and flexibility of testing equipment;
(2) Using a wireless connection testing device to measure the RF TRx characteristics of WLAN devices (supporting testing of Wi Fi 5 and Wi Fi 6, as well as signaling testing of Wi Fi 6E)
a) Test the receiver sensitivity and transmission power under communication by counting data frames and ACK frames of the device;
b) Remote control and display of measurement results through a web browser with a built-in network server;
c) Use the frame capture and recording function of the device to troubleshoot connection issues;
d) Connect two devices to test the reception sensitivity and transmission power under 2x2 MIMO communication, and complete the RF performance evaluation of the equipment;
e) By analyzing the spectrum and modulation of the equipment, ensure the quality of the transmitter;
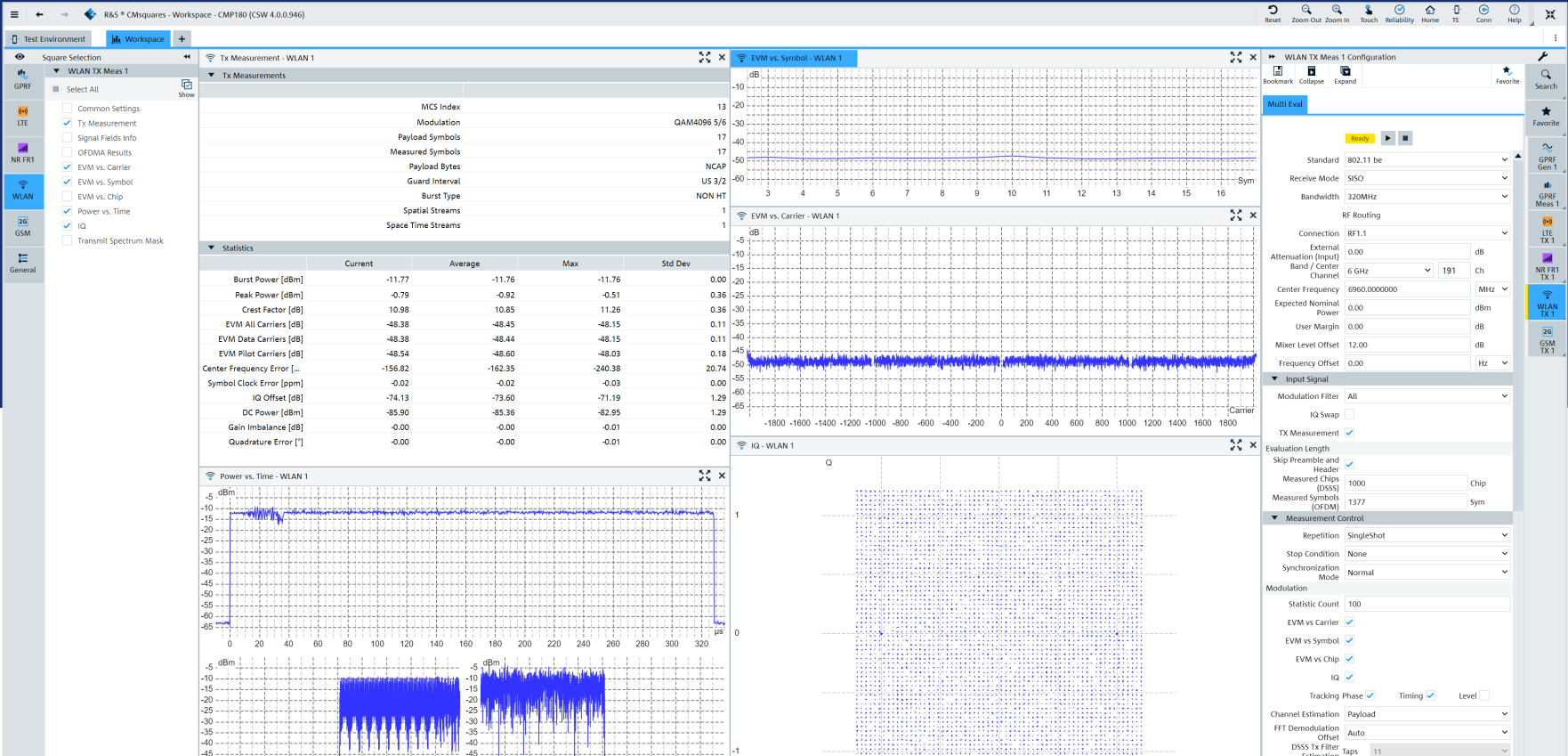
4、 The main workflow for using wireless connection testing devices
3、The main workflow of the wireless communication tester
Build a hardware environment and supporting software development platform, analyze data through a graphical user interface, complete testing projects, and view corresponding data changes by selecting the corresponding testing section in the workspace.

4、 The main workflow for using wireless connection testing devices
By using network mode, RF TRx characteristics such as Tx power, modulation accuracy (EVM), etc. can be measured together with WLAN devices under actual working conditions. There is no need to put the DUT into a dedicated testing mode, directly control the DUT. The RF performance of DUT can be quantified under the firmware conditions at the time of actual shipment. At the same time, by building a hardware environment, simulating access points and sites, establishing DUT network connections using WLAN protocol messages, selecting different encryption schemes with different standard combinations, and using general communication programs for corresponding measurements.
The above is a brief introduction to Wi Fi 5, Wi Fi 6, Wi Fi 6E, and Wi Fi 7 related tests. For more testing details and test plan content, please contact Deeplight Technology for consultation.
Recommended items
-

Wi-Fi Alliance Certification
Wi-Fi Alliance is a commercial alliance that owns the Wi-Fi trademark. It is responsible for Wi-Fi certification and trademark authorizationView more -

The WIFI Alliance certification process and experience reminder
Wi-Fi Alliance certification has existed for many years as a mainstream short-range technology standard certification.As a technically complex test, Deeplight has assisted many enterprises in the world to complete certification for many years, reflecting the characteristics of our technical service....View more -

What is WIFI Alliance?
Wi-Fi Alliance (full name: International Wi-Fi Alliance Organization), English: Wi-Fi Alliance, WFA for short), is a business alliance that owns the trademark of Wi-Fi. Responsible for Wi-Fi certification and trademark authorization. The Wi-Fi certificate is promulgated by the Wi-Fi Alliance. Wi-Fi (abbreviation for Wireless Fidelity) is the standard for wireless LA...View more -

WIFI Alliance Certification
With more than ten years of working experience in this industry, we are committed to providing unique technical services in the niche testing and certification field with segmentation, high professionalism and rich experience requirements....View more